Livagen vendor/Peptide analysis/Peptide supplier
Description
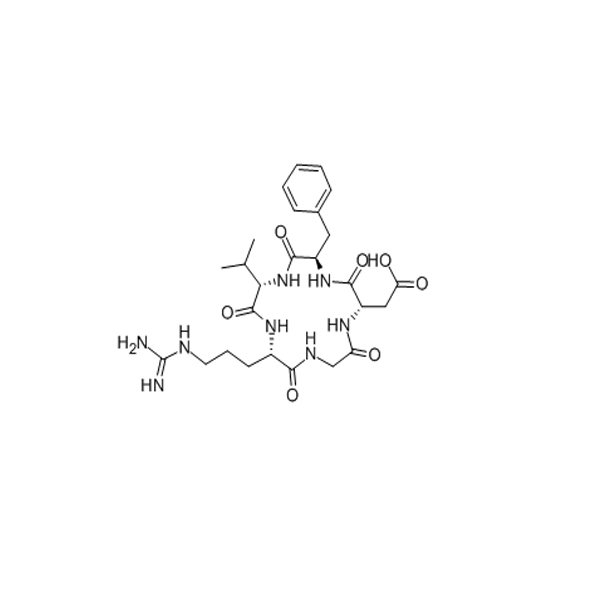
Livagen is a short-chain bioregulatory peptide, primarily known for its potential influence on DNA structure and function, particularly in relation to chromatin decondensation and gene expression.Research suggests it may stimulate the immune system and counteract diseases affecting the central nervous system, heart, gastrointestinal tract, and immunological system, primarily through its effects on lymphocytes.
Specifications
Apperance: White to off-white powder
Purity(HPLC): ≥98.0%
Single Impurity: ≤2.0%
Acetate Content(HPLC): 5.0%~12.0%
Water Content (Karl Fischer): ≤10.0%
Peptide Content: ≥80.0%
Packing and Shipping: Low temperature, vacuum packing, accurate to mg as required.
FAQ:
Which modified labeled polypeptides can be synthesized in Chinese peptide?
Our company provides a variety of modified peptide labeling, such as acetylation, biotin labeling, phosphorylation modification, fluorescence modification, can also be customized according to your special needs.
How do you dissolve polypeptides?
The solubility of polypeptide depends mainly on its primary and secondary structure, the nature of modification label, solvent type and final concentration. If the peptide is insoluble in water, ultrasound can help dissolve it. For basic peptide, it is recommended to dissolve with 10% acetic acid; For acidic peptides, dissolution with 10%NH4HCO3 is recommended. Organic solvents can also be added to insoluble polypeptides. The peptide is dissolved in the least amount of organic solvent (e.g., DMSO, DMF, isopropyl alcohol, methanol, etc.). It is highly recommended that the peptide be dissolved in the organic solvent first and then slowly added to water or other buffer until the desired concentration.
Which end is best for my research?
By default, the peptide ends with an N-terminal free amino group and a C-terminal free carboxyl group. The peptide sequence often represents the sequence of the mother protein. In order to be closer to the mother protein, the end of the peptide often needs to be closed, that is, n-terminal acetylation and C-terminal amidation. This modification avoids the introduction of excess charge, and also makes it more able to prevent exonucliase action, so that the peptide is more stable.
What is net weight? What is peptide content?
After lyophilized peptide is generally fluffy and fluff-like, it may still contain trace amounts of water, adsorbed solvents and salts due to the characteristics of peptide itself. This does not mean that the purity of the peptide is not enough, but that the actual content of the peptide is reduced by 10% to 30%. The net weight of the peptide is the actual weight of the peptide minus the water and protonated ions. In order to ensure the concentration of peptide, the non-peptide substances need to be removed from the crude peptide.
How is my peptide transported? What test reports are provided?
All freeze-dried polypeptides are usually stored in special containers of 2 ml or 10ml with original analytical data and synthesis reports containing important information such as sequence, molecular weight, purity, weight, and number of the polypeptide.