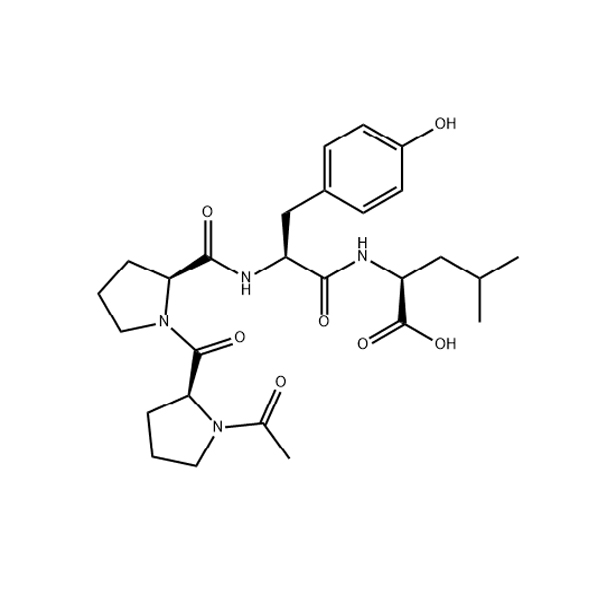
Nonapeptide-3 vendor/123167-52-2/Peptide supplier
Description
Nonapeptide-3 is a synthetic peptide used in skincare for its anti-aging and skin-conditioning properties. It is designed to mimic the effects of retinol (Vitamin A) but without the potential irritation.Nonapeptide-3 functions by mimicking the activity of retinoic acid, the active form of retinol. It does this by upregulating certain genes in the skin that are also influenced by retinoic acid. This leads to increased cell turnover and collagen production, resulting in a smoother, more youthful appearance.
Specifications
Apperance: White to off-white powder
Purity(HPLC): ≥98.0%
Single Impurity: ≤2.0%
Acetate Content(HPLC): 5.0%~12.0%
Water Content (Karl Fischer): ≤10.0%
Peptide Content: ≥80.0%
Packing and Shipping: Low temperature, vacuum packing, accurate to mg as required.
FAQ:
I need a cyclic peptide, which contains a tryptophan, will it be oxidized?
The oxidation of tryptophan is a common phenomenon in peptide oxidation, and peptides are usually cyclized before purification. If the oxidation of tryptophan occurs, the retention time of the peptide on the HPLC column will change, and the oxidation can be removed by purification. Furthermore, oxidized peptides can also be detected by MS.
Are polypeptides harmful to humans?
Peptides, which are naturally present in the human body, are generally safe for use. However, some peptides may have specific pharmacological activities, and it is advisable to consult with a doctor or a professional before using them.
What are the differences between peptides and proteins?
Peptides and proteins are both composed of amino acids, but they differ in molecular weight and length. Generally, those with a molecular weight less than 10,000 daltons (Da) and shorter amino acid chains are called peptides, while those with a larger molecular weight and longer amino acid chains are referred to as proteins.
What are the applications of peptide libraries?
Peptide libraries are an efficient tool for many studies, including GPCR ligand screening, protein-protein interaction studies, functional proteomics, nucleotide binding, screening of enzymatically acting substrates and inhibitors, antigen and epitope screening, signaling molecule search, and other important processes of drug screening.
What are the best preservation conditions? How stable is the peptide?
After lyophilized, polypeptide can form fluff or flocculant powder, which can avoid premature degradation of polypeptide. Recommended storage conditions: a. -20℃ storage or dry environment b. Try to avoid repeated freeze-thaw c. Try to avoid storage in solution state (freeze-dried powder can be stored in separate packages for convenience of use) d. If it must be stored in solution, it is recommended to dissolve the peptides in sterile water under weakly acidic conditions and store at -20℃.