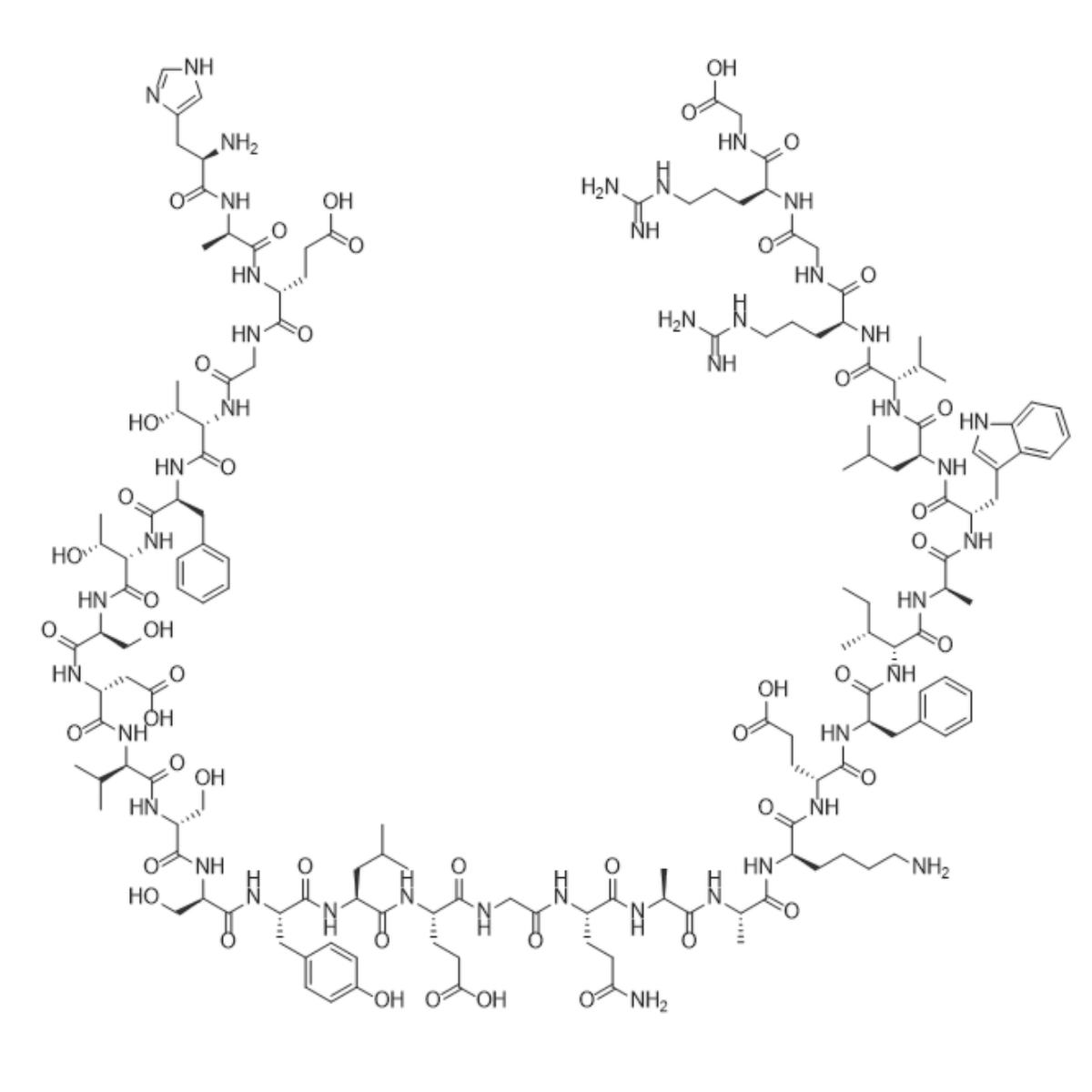
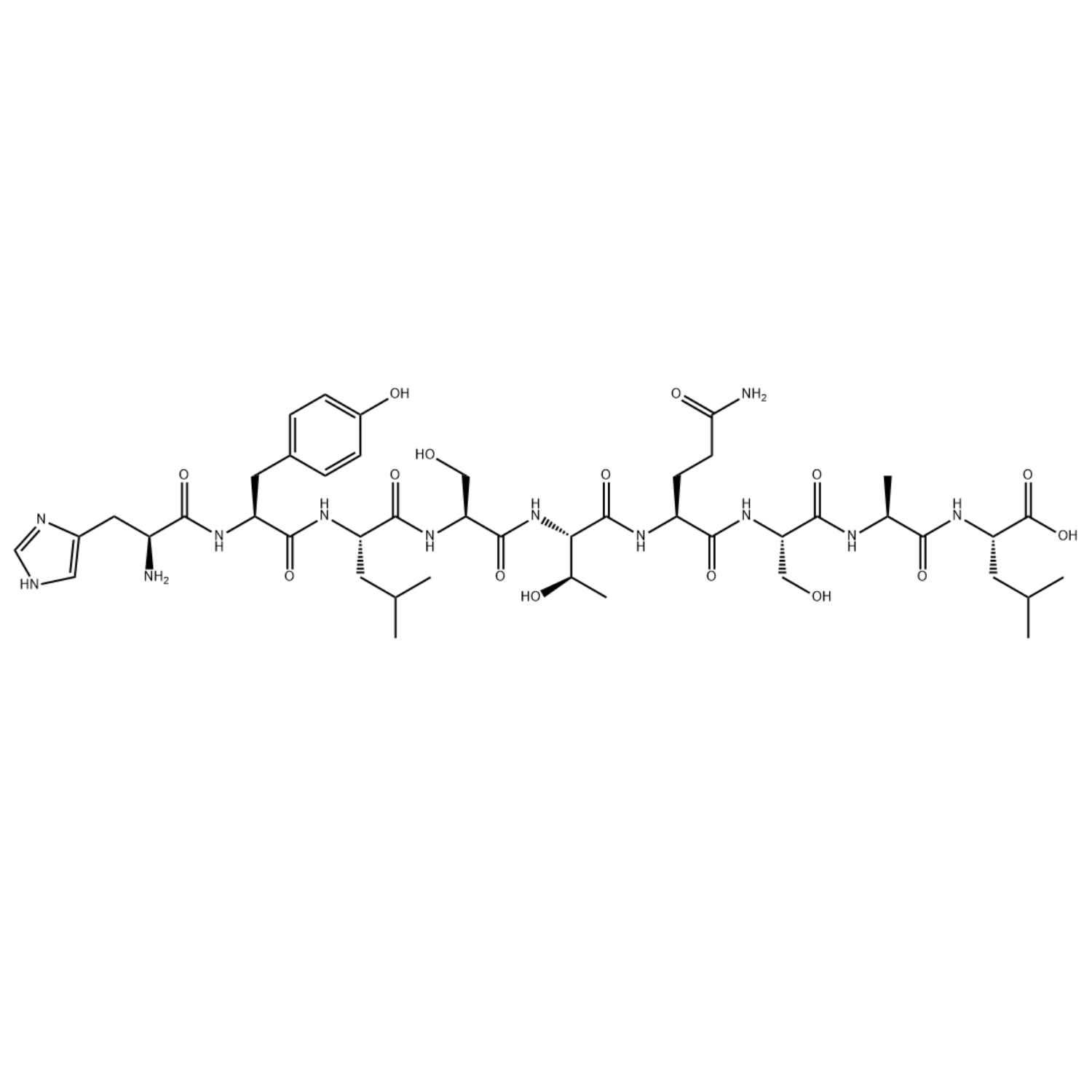
Arg(34)GLP-1(7-37)/204521-68-6/Peptide purification
Arg(34)GLP-1(7-37) is the liraglutide intermediate sequence, where the amino acid at position 34 becomes arginine, and it is a linear polypeptide composed of 31 amino acids.
Specifications
Apperance: White to off-white powder
Purity(HPLC): ≥98.0%
Single Impurity: ≤2.0%
Acetate Content(HPLC): 5.0%~12.0%
Water Content (Karl Fischer): ≤10.0%
Peptide Content: ≥80.0%
Packing and Shipping: Low temperature, vacuum packing, accurate to mg as required.
FAQ:
How do you dissolve polypeptides?
The solubility of polypeptide depends mainly on its primary and secondary structure, the nature of modification label, solvent type and final concentration. If the peptide is insoluble in water, ultrasound can help dissolve it. For basic peptide, it is recommended to dissolve with 10% acetic acid; For acidic peptides, dissolution with 10%NH4HCO3 is recommended. Organic solvents can also be added to insoluble polypeptides. The peptide is dissolved in the least amount of organic solvent (e.g., DMSO, DMF, isopropyl alcohol, methanol, etc.). It is highly recommended that the peptide be dissolved in the organic solvent first and then slowly added to water or other buffer until the desired concentration.
How do I store peptides?
Usually the peptide product you receive is lyophilized powder packaging, please store the peptide in a dry, dark -20°C freezer immediately after receiving the sample to maintain the peptide stability as much as possible. Before use, place the polypeptide packaging tube from the freezer to a dry condition at room temperature, and allow the temperature to naturally warm to room temperature before opening the cap. Otherwise, water vapor in the air will enter the sample tube when the lid is opened, reducing peptide stability. Once opened, it should be weighed quickly and immediately sealed to avoid deliquescent, and hydrophilic peptides should be more careful to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Outside temperature during short-term transportation will not affect the shelf life and quality of peptides.
What is Net Peptide Content?
It is important to understand the difference between net peptide content and total peptide weight (gross weight). In general, peptide lyophilized powder samples contain not only peptides, but also other substances such as water, solvents absorbed by peptides, counterions, and salts. The total peptide weight (gross weight) refers to the weight of all these mixtures. The net peptide content is relative to the non-peptide substances, balanced ions and water, and after removing these, the remaining is the net peptide content. The net peptide content can be determined by nitrogen analysis or amino acid composition analysis, usually accounting for 50-80% of the total peptide weight. Net peptide content is different from peptide purity, which refers to the percentage of peptide of interest in a sample.
Why should peptides be modified by N-terminal acetylation and C-terminal amidation?
Such modifications can give peptide sequences properties that are native to proteins.
What are peptides?
Peptides are short chain molecules formed by amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. They typically consist of 2 to 70 amino acids.