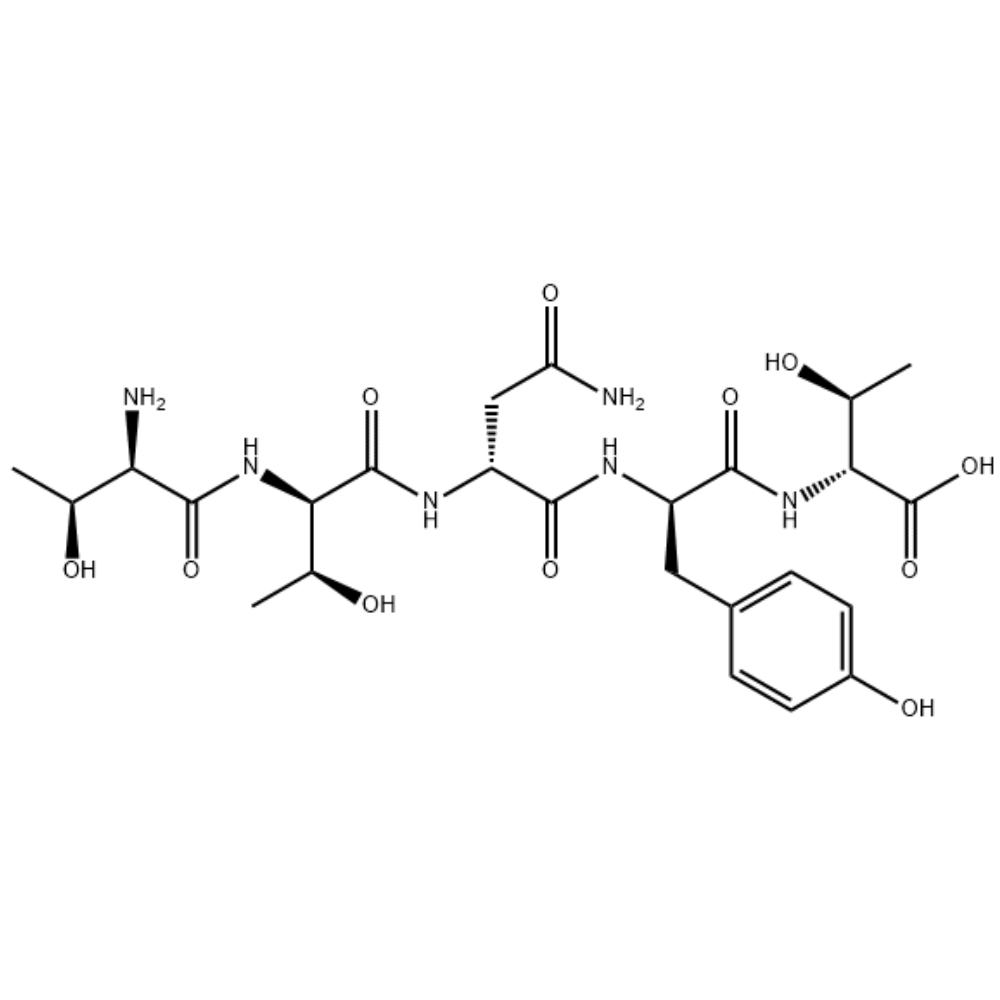
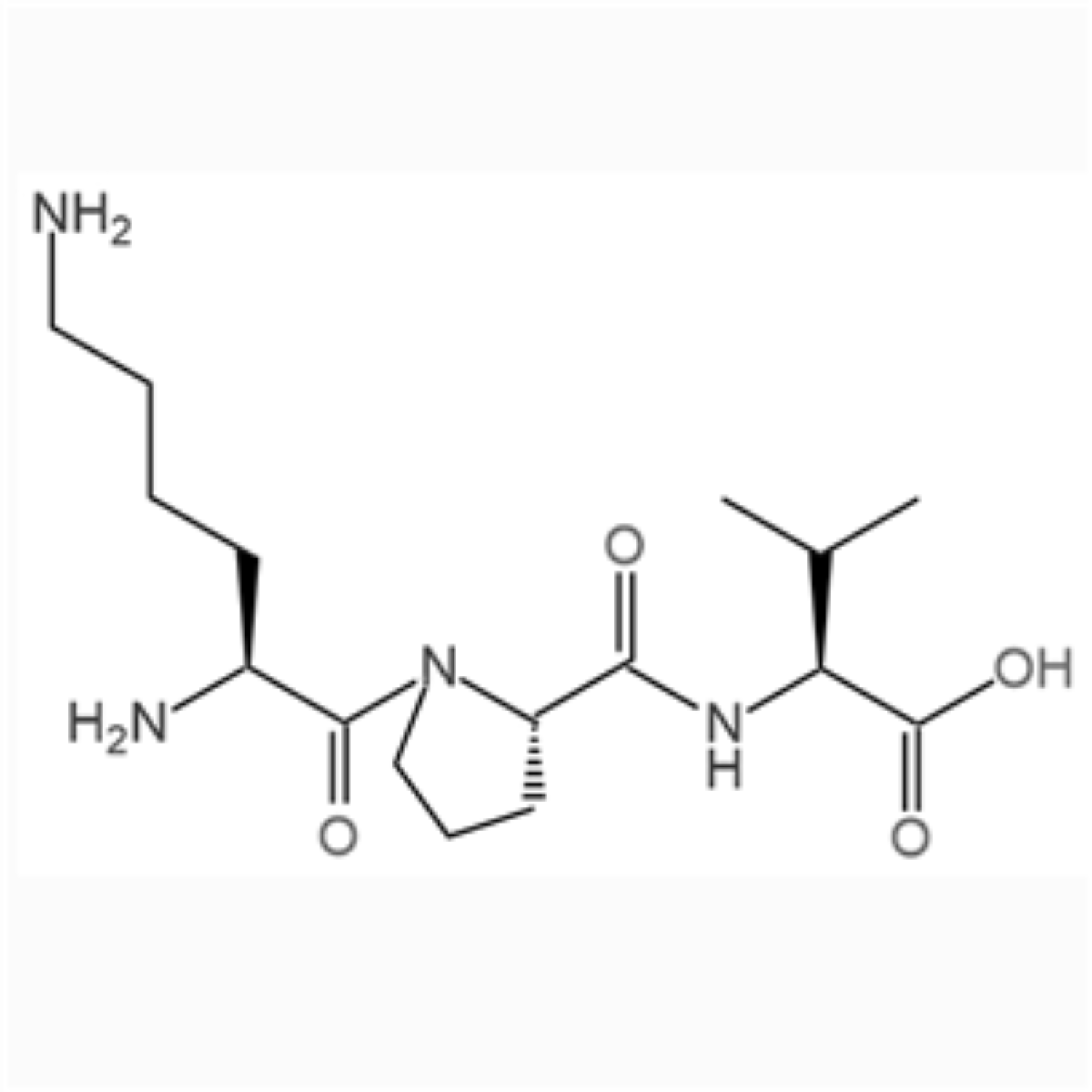
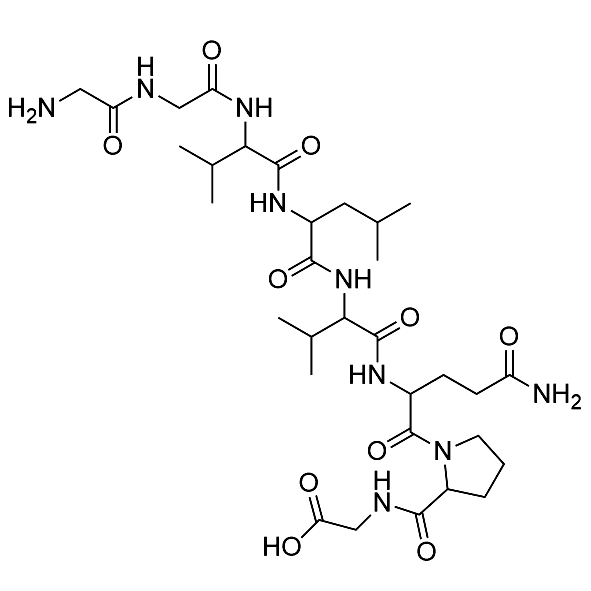
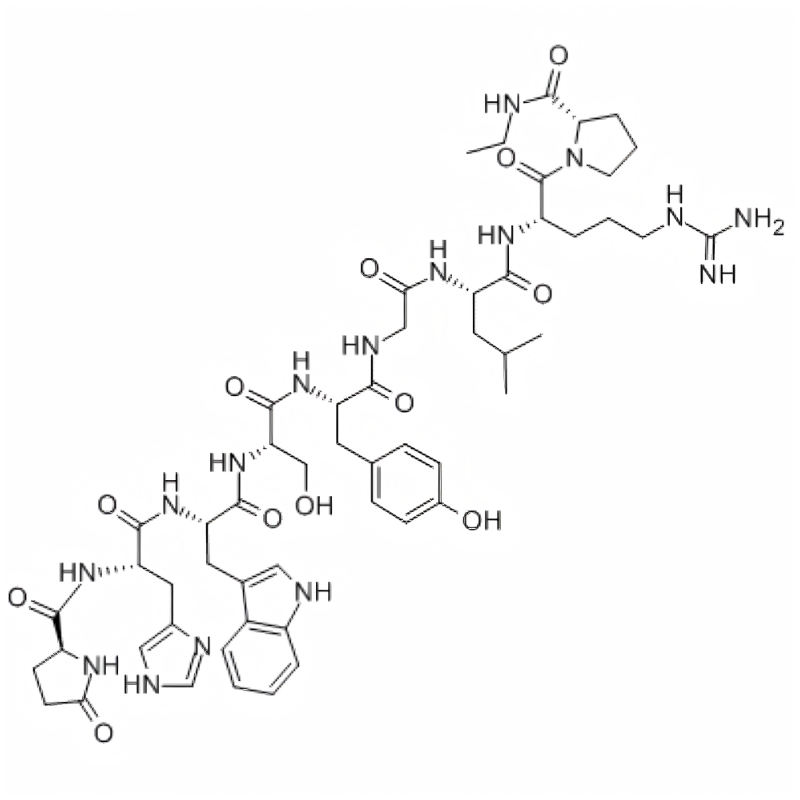
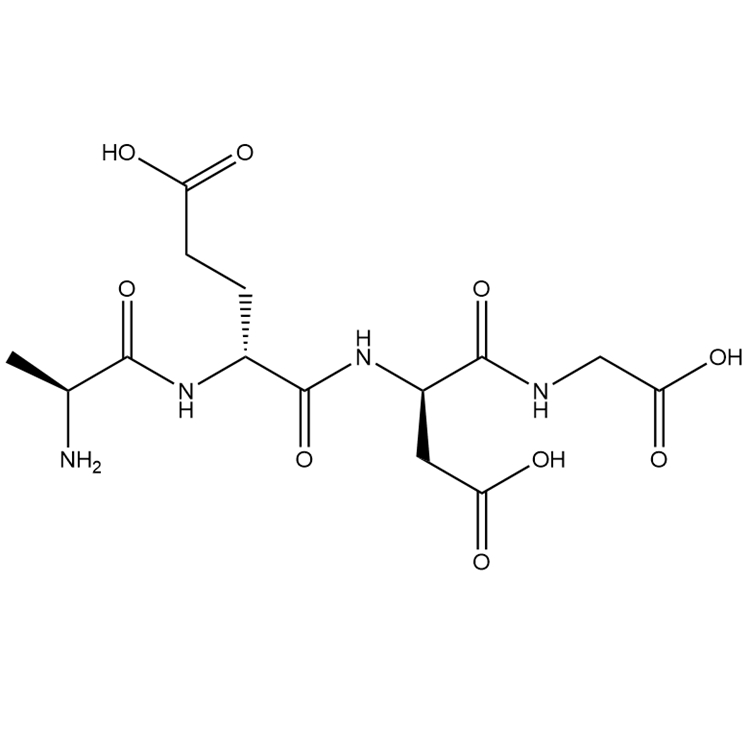
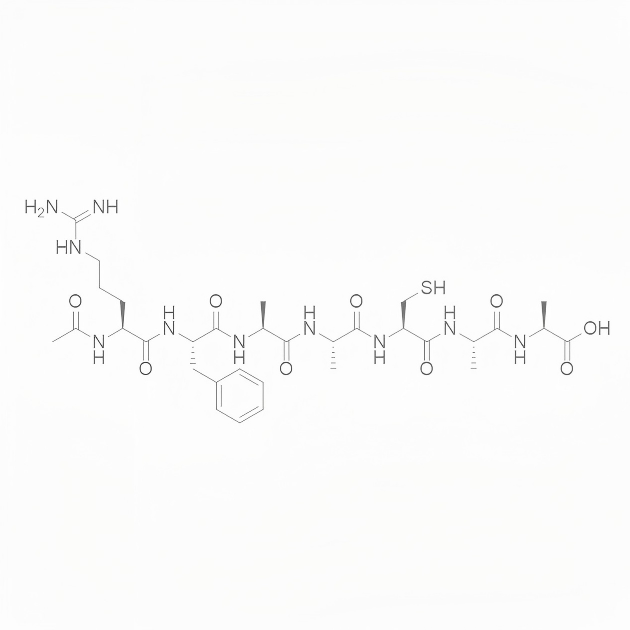
RAP-103/1337998-99-8/Peptide customization
Description
RAP-103 is an orally active CCR antagonist composed of five D-type amino acids, providing effective synaptic protection by inhibiting and reversing PrPC/NOX signaling-induced cytoskeletal changes. RAP-103 has potential for the study of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Specifications
Apperance: White to off-white powder
Purity(HPLC): ≥98.0%
Single Impurity: ≤2.0%
Acetate Content(HPLC): 5.0%~12.0%
Water Content (Karl Fischer): ≤10.0%
Peptide Content: ≥80.0%
Packing and Shipping: Low temperature, vacuum packing, accurate to mg as required.
FAQ:
What are the uses of peptides?
Peptides have a wide range of applications in the biomedical field, including:
Drug development: Peptides can be used as lead compounds for drugs or directly as drugs themselves.
Vaccines: Peptides can be used as antigens for vaccine preparation.
Biomaterials: Peptides can be used to construct biomaterials, such as scaffolds for tissue engineering.
Diagnostic reagents: Peptides can be used in the development of diagnostic reagents, such as those for detecting disease-related proteins.
Cosmetics: Certain peptides have moisturizing, anti-aging, and whitening effects and can be added to cosmetics.
I need a cyclic peptide, which contains a tryptophan, will it be oxidized?
The oxidation of tryptophan is a common phenomenon in peptide oxidation, and peptides are usually cyclized before purification. If the oxidation of tryptophan occurs, the retention time of the peptide on the HPLC column will change, and the oxidation can be removed by purification. Furthermore, oxidized peptides can also be detected by MS.
What is net weight? What is peptide content?
After lyophilized peptide is generally fluffy and fluff-like, it may still contain trace amounts of water, adsorbed solvents and salts due to the characteristics of peptide itself. This does not mean that the purity of the peptide is not enough, but that the actual content of the peptide is reduced by 10% to 30%. The net weight of the peptide is the actual weight of the peptide minus the water and protonated ions. In order to ensure the concentration of peptide, the non-peptide substances need to be removed from the crude peptide.
What are small molecular peptides?
Peptides are formed by multiple amino acids connected through peptide bonds. The difference from proteins is the number of amino acids that make up the molecule. Oligopeptides, consisting of 2-9 amino acids, are also known as small molecular peptides, with an average molecular weight of amino acids being 128 Da. Therefore, the molecular weight of oligopeptides is generally less than 1000 Da.