Solnatide supplier/259206-53-6/Peptide supplier
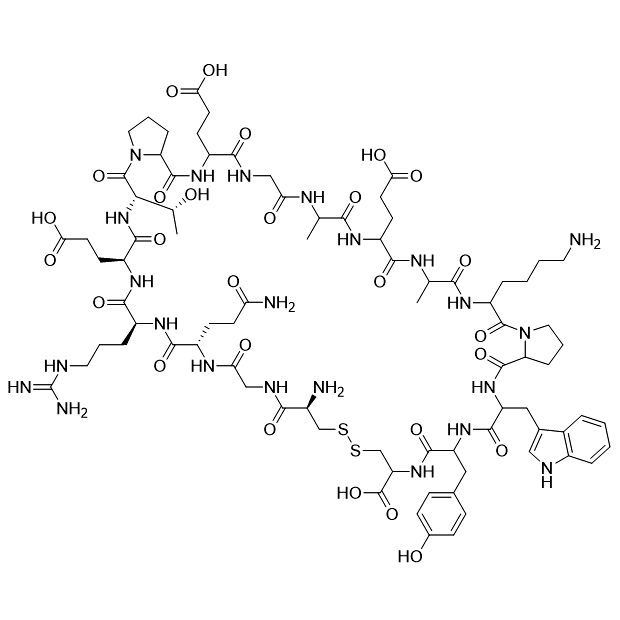
Solnatide is a cyclic peptide which is composed of 17 amino acids and also contains a pair of disulfide bonds in its peptide sequence. Solnatide has certain advantages in maintaining biological stability and can accelerate the clearance of alveolar fluid in clinical trials. Clinically, Solnatide can restore physiological lung function in patients with pulmonary edema (those undergoing mechanical ventilation) and in patients with primary graft dysfunction (caused by lung transplantation).
Specifications
Apperance: White to off-white powder
Purity(HPLC): ≥98.0%
Single Impurity: ≤2.0%
Acetate Content(HPLC): 5.0%~12.0%
Water Content (Karl Fischer): ≤10.0%
Peptide Content: ≥80.0%
Packing and Shipping: Low temperature, vacuum packing, accurate to mg as required.
FAQ:
What are the advantages of PEG-modified peptides?
Polyethylene glycol modification is the addition of a polymer (ethylene glycol) to the target molecule by means of covalent bonding. By camouflaging the peptide, the PEG modification fools the host cell's immune system, enhances the therapeutic effect of the peptide, and increases the solubility and bioavailability of the hydrophobic drug. It can also prolong the circulation time of polypeptides by decreasing renal clearance.
What is Net Peptide Content?
It is important to understand the difference between net peptide content and total peptide weight (gross weight). In general, peptide lyophilized powder samples contain not only peptides, but also other substances such as water, solvents absorbed by peptides, counterions, and salts. The total peptide weight (gross weight) refers to the weight of all these mixtures. The net peptide content is relative to the non-peptide substances, balanced ions and water, and after removing these, the remaining is the net peptide content. The net peptide content can be determined by nitrogen analysis or amino acid composition analysis, usually accounting for 50-80% of the total peptide weight. Net peptide content is different from peptide purity, which refers to the percentage of peptide of interest in a sample.
What is the direction of synthesis of peptides?
Peptide synthesis is from the C-terminus to the N-terminus of the polypeptide.
What is net weight? What is peptide content?
After lyophilized peptide is generally fluffy and fluff-like, it may still contain trace amounts of water, adsorbed solvents and salts due to the characteristics of peptide itself. This does not mean that the purity of the peptide is not enough, but that the actual content of the peptide is reduced by 10% to 30%. The net weight of the peptide is the actual weight of the peptide minus the water and protonated ions. In order to ensure the concentration of peptide, the non-peptide substances need to be removed from the crude peptide.
How do you dissolve polypeptides?
The solubility of polypeptide depends mainly on its primary and secondary structure, the nature of modification label, solvent type and final concentration. If the peptide is insoluble in water, ultrasound can help dissolve it. For basic peptide, it is recommended to dissolve with 10% acetic acid; For acidic peptides, dissolution with 10%NH4HCO3 is recommended. Organic solvents can also be added to insoluble polypeptides. The peptide is dissolved in the least amount of organic solvent (e.g., DMSO, DMF, isopropyl alcohol, methanol, etc.). It is highly recommended that the peptide be dissolved in the organic solvent first and then slowly added to water or other buffer until the desired concentration.


![CecropinA-melittinhybridpeptide[CA(1-7)M(2-9)NH2] /157606-25-2/GT Peptide/Peptide Supplier](https://www.gtpeptide.com/uploadfile/202506/e5e50c035840935.jpg)

