Survodutide supplier/2805997-46-8/Peptide R&D
Description
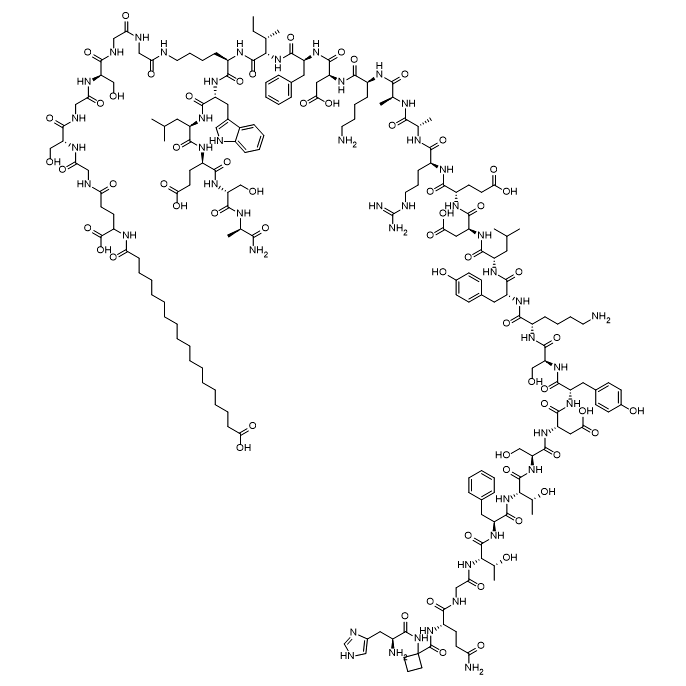
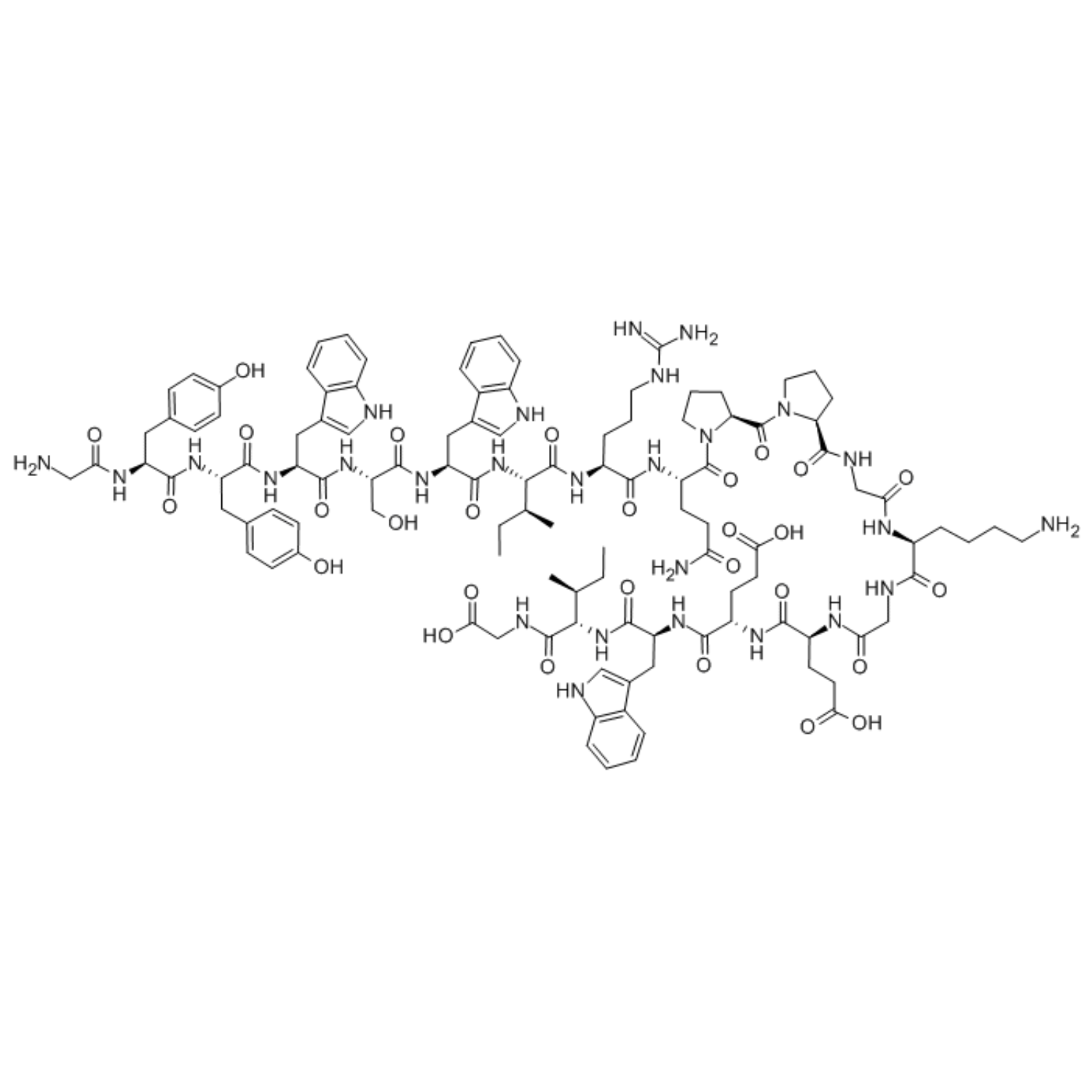
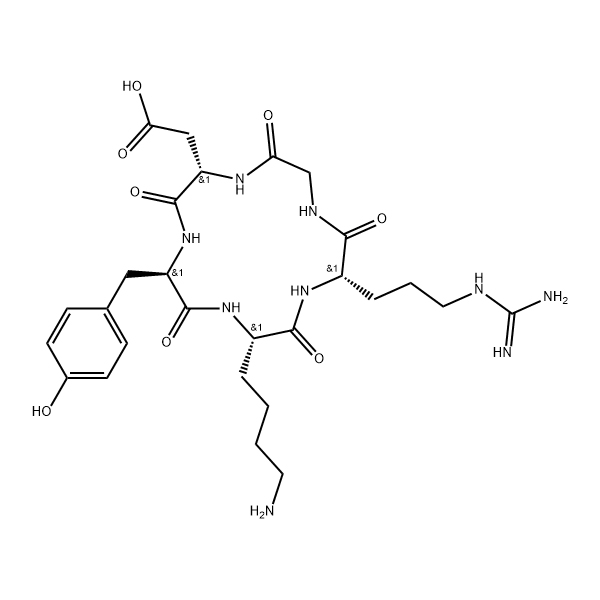
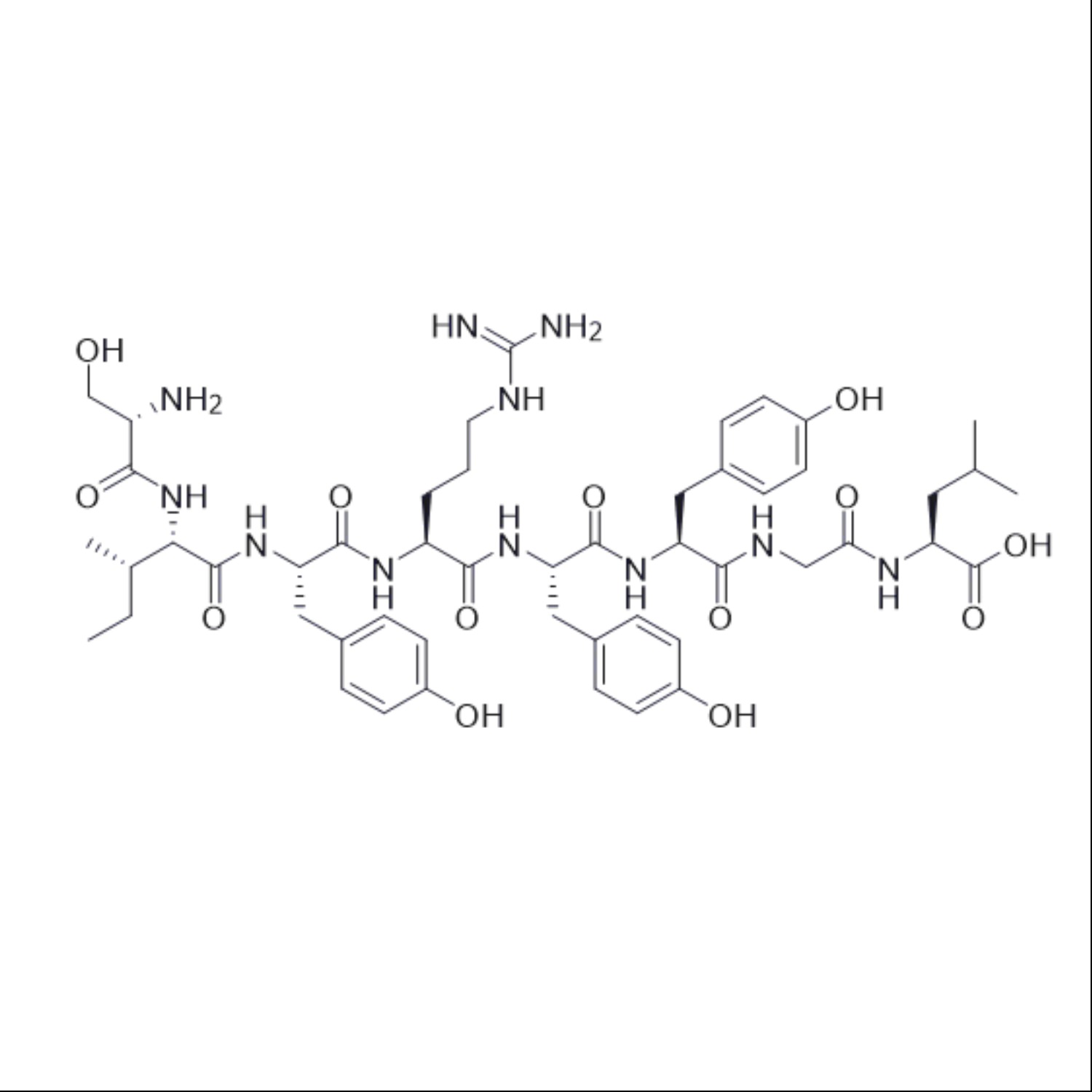
Survodutide is an effective, selective glucagon and GLP-1 receptor agonist peptide. It consists of 35 amino acids and includes side chain structures in its sequence. Survodutide exerts powerful anti-obesity effects by increasing energy expenditure and reducing food intake.
Specifications
Apperance: White to off-white powder
Purity(HPLC): ≥98.0%
Single Impurity: ≤2.0%
Acetate Content(HPLC): 5.0%~12.0%
Water Content (Karl Fischer): ≤10.0%
Peptide Content: ≥80.0%
Packing and Shipping: Low temperature, vacuum packing, accurate to mg as required.
FAQ:
What is the direction of synthesis of peptides?
Peptide synthesis is from the C-terminus to the N-terminus of the polypeptide.
What are the advantages of Pharmaceutical Peptide?
The rapid development of Pharmaceutical Peptide benefits from their significant advantages:
• Significant activity, relatively strong specificity, good affinity for receptors, lower toxicity, and not easily accumulating in the body;
• Compared to protein-based macromolecular drugs, except for peptide vaccines, peptide drugs have relatively low immunogenicity, require smaller dosages, and have higher unit activity;
• Easy to modify and produce, and can even be addressed through synthetic methods.
How do you dissolve polypeptides?
The solubility of polypeptide depends mainly on its primary and secondary structure, the nature of modification label, solvent type and final concentration. If the peptide is insoluble in water, ultrasound can help dissolve it. For basic peptide, it is recommended to dissolve with 10% acetic acid; For acidic peptides, dissolution with 10%NH4HCO3 is recommended. Organic solvents can also be added to insoluble polypeptides. The peptide is dissolved in the least amount of organic solvent (e.g., DMSO, DMF, isopropyl alcohol, methanol, etc.). It is highly recommended that the peptide be dissolved in the organic solvent first and then slowly added to water or other buffer until the desired concentration.
What are small molecular peptides?
Peptides are formed by multiple amino acids connected through peptide bonds. The difference from proteins is the number of amino acids that make up the molecule. Oligopeptides, consisting of 2-9 amino acids, are also known as small molecular peptides, with an average molecular weight of amino acids being 128 Da. Therefore, the molecular weight of oligopeptides is generally less than 1000 Da.
What is a peptide?
A peptide is a compound formed by α-amino acids connected by peptide bonds and is an intermediate product of protein hydrolysis. A compound formed by the dehydration condensation of two amino acid molecules is called a dipeptide, and similarly, there are tripeptides, tetrapeptides, pentapeptides, etc. A peptide composed of three or more amino acid molecules is called a polypeptide.