Amino acids form polypeptide proteins through condensation reactions, following certain rules. This process involves complex chemical reactions in which amino acid molecules are linked into a chain-like structure via dehydration condensation, ultimately resulting in polypeptide proteins with specific functions. Through dehydration condensation, peptide bonds are formed between amino acids. This crucial step enables amino acids to be connected in a specific sequence and manner, thereby constructing complex polypeptide protein structures. After dehydration condensation, the peptide bond formed between amino acids can be abbreviated as "—CONH—", but it should be noted that it cannot be abbreviated as "—CNHO—".
1.Condensation Mechanism and Polypeptide Formation
Amino acids form polypeptides through condensation reactions. In this process, amino acids are linked into chain-like structures via dehydration condensation, resulting in polypeptides with specific functions, among which the formation of peptide bonds is of critical importance.
2.Intermolecular Condensation Process
In the dehydration condensation reaction of amino acids, the amino group of one amino acid molecule reacts with the carboxyl group of another amino acid molecule. Through an intermolecular dehydration process, they collectively form a peptide bond. In dehydration condensation, the amino group and carboxyl group of amino acid molecules react to create peptide bonds, which can occur between either different or identical amino acids.When two distinct amino acids, A and B, combine to form a dipeptide, possible scenarios include:The amino group of amino acid A reacts with the carboxyl group of amino acid B, resulting in the removal of a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group to form a peptide bond.Alternatively, the carboxyl group of amino acid A reacts with the amino group of amino acid B, similarly removing a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group to construct the peptide bond.Additionally, another possibility exists: two identical amino acid molecules, whether AA or BB, can also form peptide bonds through analogous dehydration reactions.
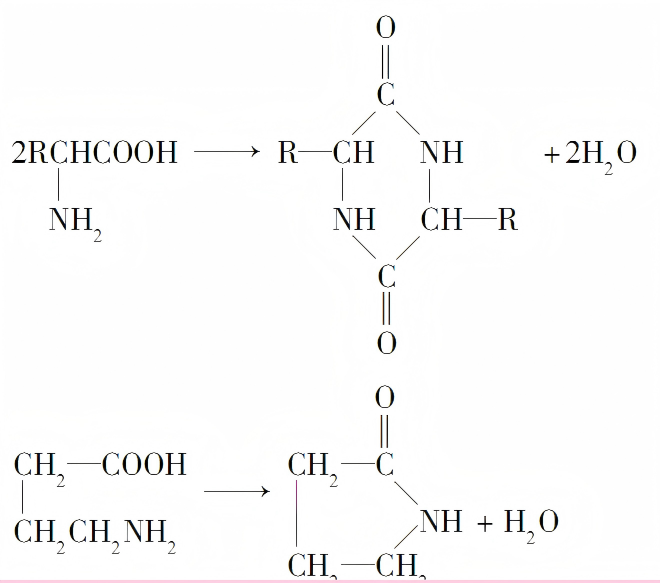
3.Cyclization Reaction
During the dehydration condensation of amino acids, in addition to conventional reactions such as dipeptide formation, a special cyclization reaction may occur. This reaction can take place either intermolecularly or intramolecularly, resulting in the formation of cyclic structures through condensation. Cyclization in dehydration condensation can create ring-shaped structures, and this reaction is not limited to intermolecular processes but can also occur intramolecularly, producing complex structures.
4.Polycondensation Reaction and Polypeptide/Protein Formation
In the dehydration condensation process of amino acids, polycondensation reactions can further generate polypeptides and even proteins. This reaction not only involves intermolecular or intramolecular condensation cycles but also encompasses more complex chemical processes, holding significant importance for understanding protein synthesis in biological systems.
Post time: 2025-12-12
