What are antimicrobial peptides?
Antimicrobial peptides, also known as antimicrobial peptides, are an important part of the human innate immune system. They are widely present in natural organisms and are small biologically active peptides produced by organisms. The human body mainly produces two types of antimicrobial peptides: Defensin and Cathelicidin. Defensin includes various antimicrobial peptides, while Cathelicidin has only one antimicrobial peptide product—LL-37.
What is LL-37?
LL-37 is the only Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide present in the human body. It is composed of 37 amino acids at the N-terminal of the Cathelicidin protein, and its initial amino acids are L-L, hence the name LL-37.
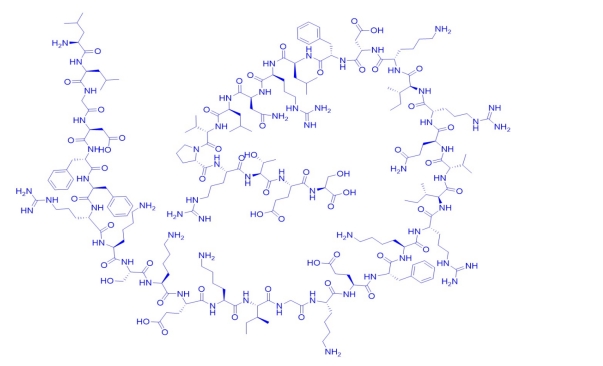
LL-37 is the main protein in neutrophils and is widely present in neutrophils, bone marrow, cervical, and vaginal squamous epithelia. The precursor of LL-37 consists of a signal peptide, a conserved cathelin domain, and 37 amino acid residues. When cells are activated, bioactive LL-37 is produced through cleavage by serine protease 3 and other proteolytic enzymes, possessing antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral functions, as well as chemotactic and immunostimulatory/regulatory functions.
Post time: 2025-10-13
