The Limulus reagent tripeptide is a tripeptide substance with a specific sequence extracted from horseshoe crab blood cell lysate or artificially synthesized. The Limulus reagent tripeptide is a chromogenic substrate used for quantitative analysis (such as the bacterial endotoxin test) to detect and measure the components of Gram-negative bacteria—endotoxins. When acted upon by enzymes activated by endotoxins, a colored compound (such as p-nitroaniline) is released, allowing the color intensity to be measured and correlated with the endotoxin content.
Working Principle
Endotoxin Activation: In the presence of endotoxins, amebocytes in horseshoe crab blood release enzymes, thereby triggering the coagulation cascade.
Enzyme Action: The activated enzyme (usually clotting enzyme) then acts on a chromogenic substrate.
Chromogenic Reaction: The enzyme cleaves the substrate, releasing a yellow compound called p-nitroaniline (pNA).
Quantitative Analysis: The intensity of the yellow color is proportional to the endotoxin content in the sample and is usually measured using a spectrophotometer at an absorbance of 405 nm.
Preparation Methods
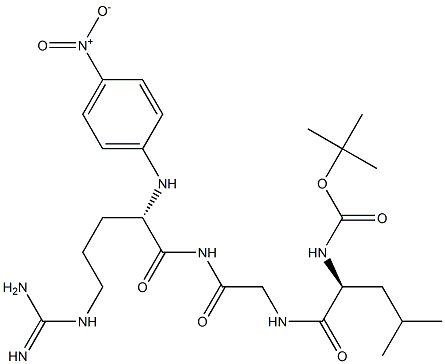
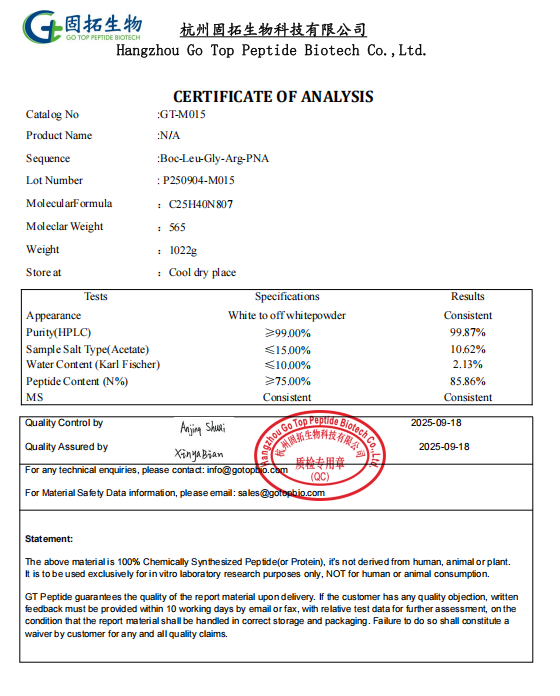
The Limulus reagent tripeptide can be obtained through two approaches in terms of preparation.
1. Extracting natural components from Limulus blood cells and obtaining the active tripeptide through separation and purification.
2. Using solid-phase synthesis technology to sequentially connect specific amino acid sequences, precisely controlling the structure of the tripeptide.
Due to the conservation policies for Limulus (with provinces such as Zhejiang, Fujian, Guangdong, and Guangxi listing it as a "provincial key protected aquatic wildlife" / Hong Kong issued regulations at the end of 2012 banning bottom trawling), and because the extraction process is complex and challenging, the cost of the first method is relatively high. Therefore, solid-phase synthesis is now commonly used. By sequentially connecting specific amino acid sequences, the structure of the tripeptide can be precisely controlled. This method not only ensures the stability and consistency of the product but also allows for large-scale production, meeting the needs of the pharmaceutical industry for testing reagents.
Post time: 2025-11-04
